Expert and lay judgments of pathogen transmission risk using visible cues

How do people conceptualize pathogen transmission risk in cities using visible cues?
Neighbourhood green spaces and wellbeing among universities students in England during the COVID-19 pandemic
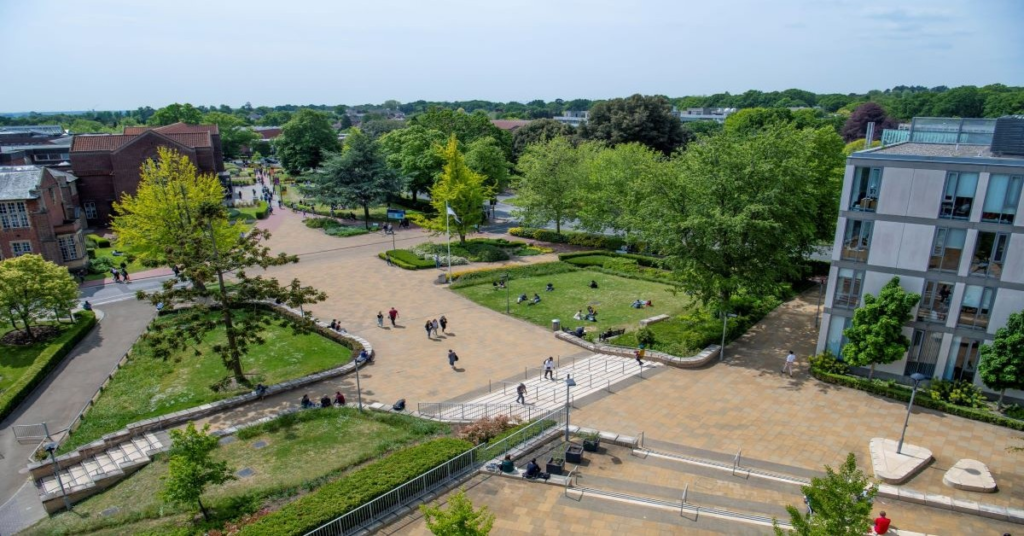

The COVID-19 pandemic restrictions and the switch to online learning impacted the life of university students. We looked at wellbeing in relation to use of greenspaces during the 3rd ‘lockdown’ in England.
Did neighbourhood amenities affect youth mental health during the pandemic?

Canadian youth who had better mental health during the first summer of the pandemic tended to also have more nearly local neighbourhood destinations.
COVID-19: Highlighting the negative impacts of odour pollution in the built environment

Odour pollution impacts our mental and physical wellbeing without being noticed very often – bad smells can have a negative impact on how we think and feel. Bad odour can affect our work and home environments in a negative way so why don’t we take it more seriously?
City compactness and COVID-19
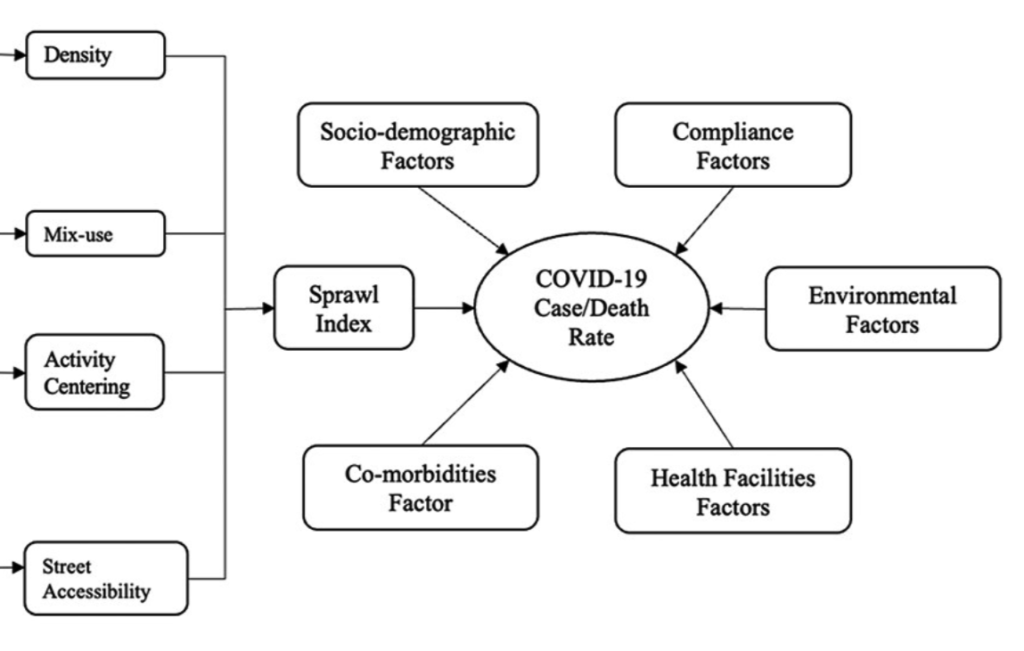
Compactness level urban areas have different health related outcomes during COVID-19.
Insights on behaviour changes, the pandemic, and the Sustainable Development Goals in Hong Kong

Our study analyzes the impact of COVID-19 on Hong Kong’s progress towards achieving the Sustainable Development Goals. The study identifies four SDGs that stood out with significant impacts from the pandemic. We offer valuable and transferable insights for policymakers and stakeholders involved in pandemic recovery and sustainable development efforts.
Mind, body and blood: investigating the changes to health and wellbeing when outdoors?
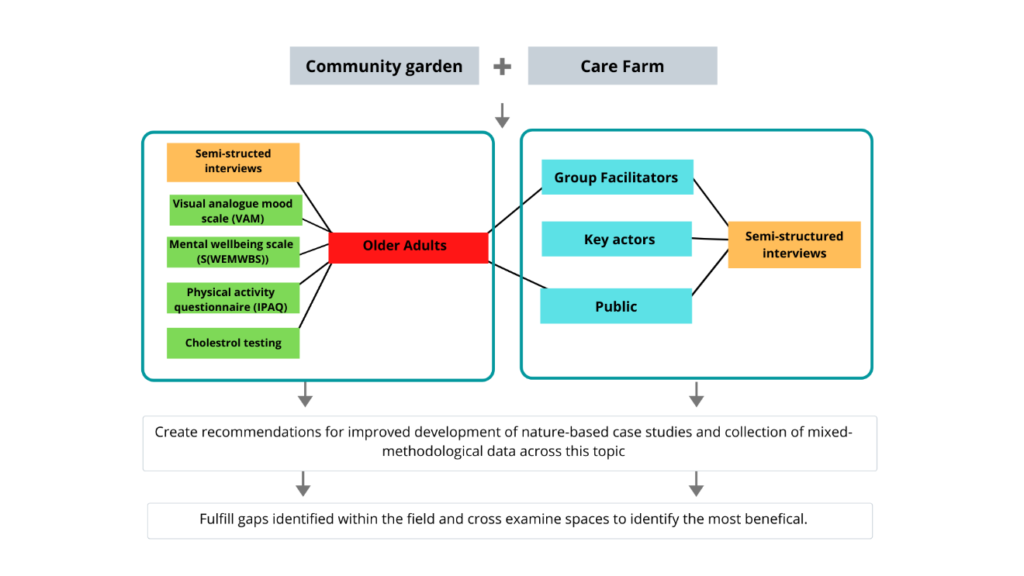
We used a case study approach to highlight potential radical health tools that could be embedded in research projects to enable us to understand more about how nature impacts health and wellbeing.
Integrating nature and workplaces in a post COVID-19 world: Building Back Better
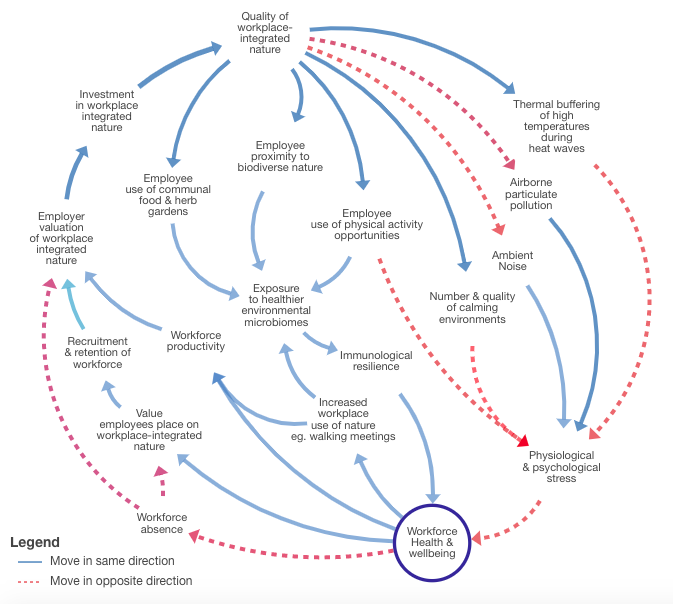
The future of workplaces now includes ‘remote’ for many, which has many health benefits. The future of ‘the office’ needs to evolve too and bringing more nature into the workplace is a healthy place to start.
Boxed in: Changes in apartment residents’ health behaviours following the COVID-19 lockdown – a longitudinal cohort study from Australia

This study adds to the literature on the health impacts of lockdowns by examining longitudinal changes in the health behaviours of Australian apartment residents. Following the COVID-19 lockdown, residents reported increased walking for recreation, sleep duration, and home cooking frequency, but decreased walking for transport, greater sitting time, and weight gain. Alcohol consumption remained stable.
What can city policy-makers do to mitigate the effects of pandemics on urban life?

By reviewing the studies on the cities in the early months of the COVID-19 outbreak, we could develop a promising perspective for identifying solutions during future similar pandemics.


