City Know-hows
Target audience
Transnational municipal networks such as C40, ICLEI Resilient Cities, UCCRN; Journalistic platforms covering cities (e.g. The Guardian, The Atlantic, Grist, Bloomberg Cities); Media-makers (e.g. How to Save a Planet podcast; OnBeing podcast; Democracy Now; All We Can Save; Heated newsletter).
The problem
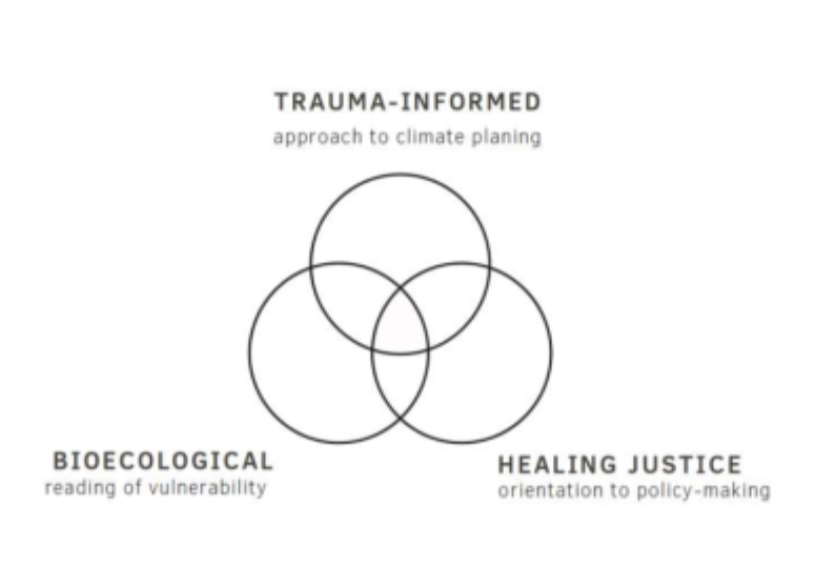
Our approach to resilience and vulnerability is narrow and outdated. It barely considers the health implication of climate change on urban populations, and even less so its mental health dimensions. Climate change will likely increase exposure to trauma, so integrating the principles of trauma-informed care and healing justice is urgently needed to design meaningful interventions that foster equitable climate outcomes.
What we did and why
Investigated how ‘official’ narratives and visions of resilience, as found in municipal climate plans, compared to the needs, values, and priorities of populations on the ground – especially vulnerable groups. Convened a public workshop in case study cities to complement document review and key informant interviews with the experiences of frontline groups. Proposed the original concept of ‘integrative resilience’ to stimulate innovation among policy-makers, urban practitioners, and community leaders in transforming the way resilience is planned in cities.
Our study’s contribution
Impacts for city policy and practice
There need to be deeper understanding of local needs, values and priorities when it comes to defining and operationalizing resilience. This approach provides a blueprint for expanding current focus of climate action plans and municipal interventions, complete with preliminary recommendations for new indicators to assess population health and metrics of success. This model equally applies to systemic crises such as COVID-19.
Further information
Full research article:
Related posts

Researchers demonstrated empirically that COVID-19 lockdowns damaged mood. In fact, their results indicate that there is a negative relationship between household density and the mood

Open spaces are known to improve the health and well-being, however there are few studies from developing countries. This Nigerian study examinessocio-economic characteristics of residents, attributes and uses of neighbourhood open spaces and self-rated health.
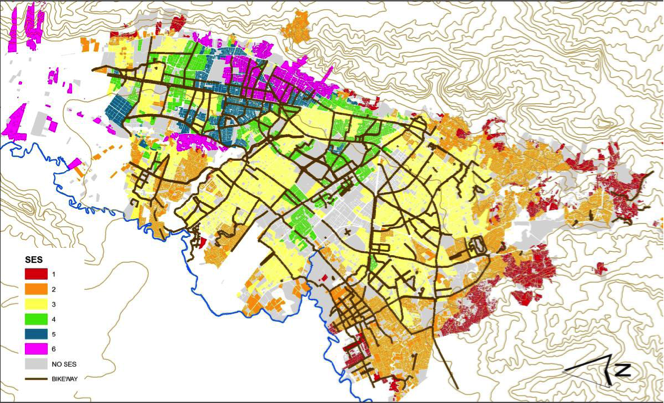
Lack of ‘Ciclorutas’ (bicycle lanes) in Bogota’s neighbourhoods of low socio-economic status shows inequality in the access to active transportation options, potentially increasing health disparities.