City Know-hows
Target audience
City council public health and transport officers
The problem
Urban health studies usually focus on the differences between neighbourhoods in the same city; however, that approach lacks any assessment of the overarching forces affecting the city as a whole.
What we did and why
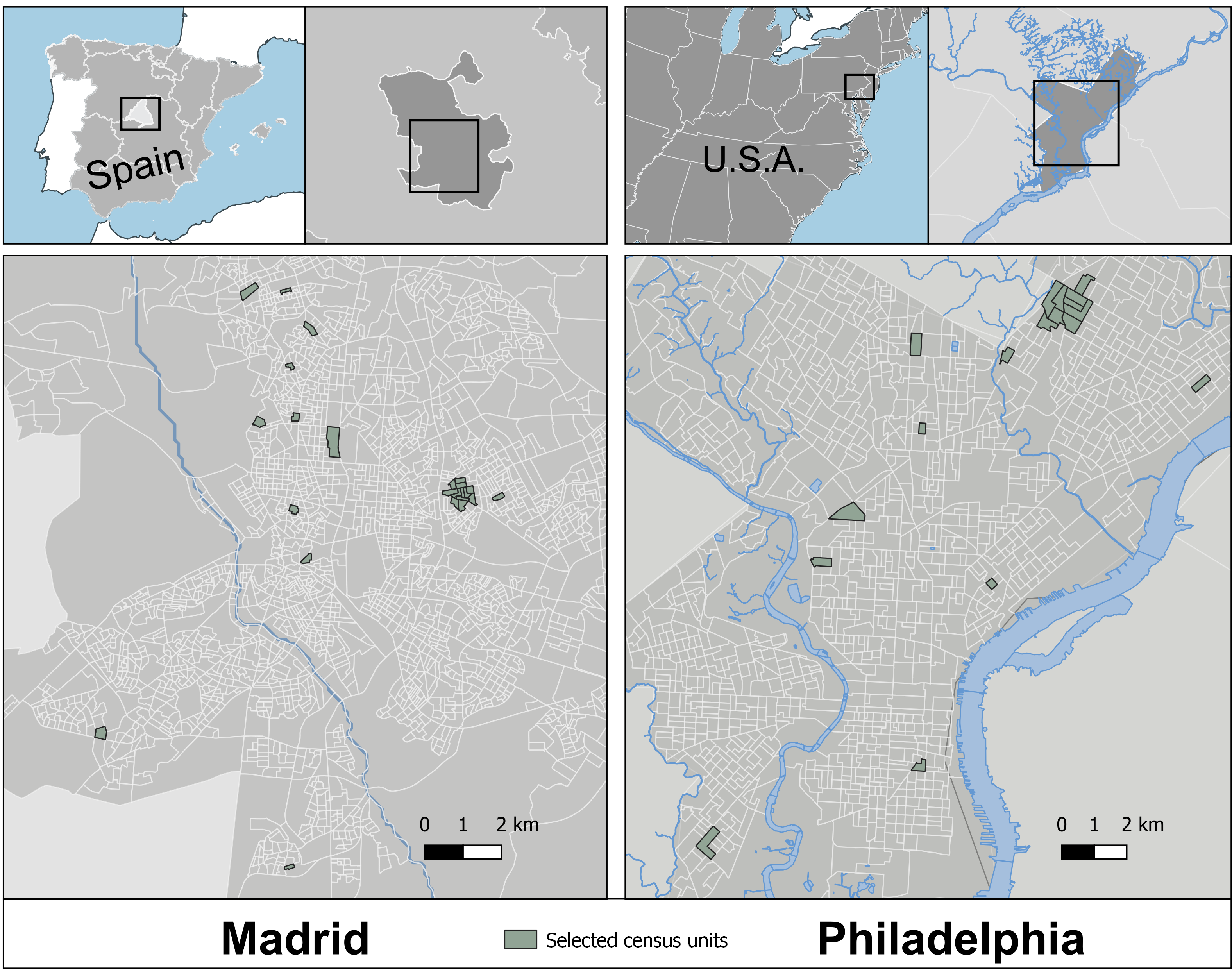
We compared differences in the walking environment between Madrid and Philadelphia. We used an audit tool called M-SPACES that measures, for each street segment;
Our study’s contribution
We found that Philadelphia’s streets had higher scores for function (physical attributes that supported walking) and safety, while Madrid streets had greater a greater proportion of streets having at least one walking destinations. These results are key to understand which elements of the built environment could be key to uncover mass influences that operate at the city level.
Impacts for city policy and practice
In order to understand which urban characteristics impact on physical activity and health, we need to understand what characterize our cities as a whole. In our study, Madrid is characterized by a higher proportion of daily walking destinations, while the streets of Philadelphia have better physical infrastructure for walking in the street.
Future studies should include attention to the potential impact of built environment characteristics at the city level.
Further information
Authors: Pedro Gullón (@pgullon), Usama Bilal (@usama_bilal), Patricia Sánchez, Julia Díez (@JuliaDiez91), Gina S. Lovasi, and Manuel Franco (@mfranco_uah)
Full research article:
Related posts
Extreme heat and wildfire smoke are a growing concern in cities. Cooling and cleaner air centres can provide a much-needed respite but too often they’re set up reactively and inconsistently. Our study explores what works, what doesn’t, and how cities can design these spaces to be reliable, inclusive, and accessible for all.

Our study explored the preferences, needs, and challenges faced by autistic children when engaging with public playgrounds. Drawing on these insights, we developed a set of evidence-based design guidelines to support neurodiverse-inclusive playgrounds through an autism-friendly, attuned co-creation methodology.

Understanding how urban environments affect health is the first step in making a healthy city.