City Know-hows
Target audience
City planners, local councils, general public, environmental psychology researchers
The problem
Much of the current public health and environmental psychology research regarding health and wellbeing is geographically restrained and unable to make direct cross-cultural comparisons between populations.
What we did and why
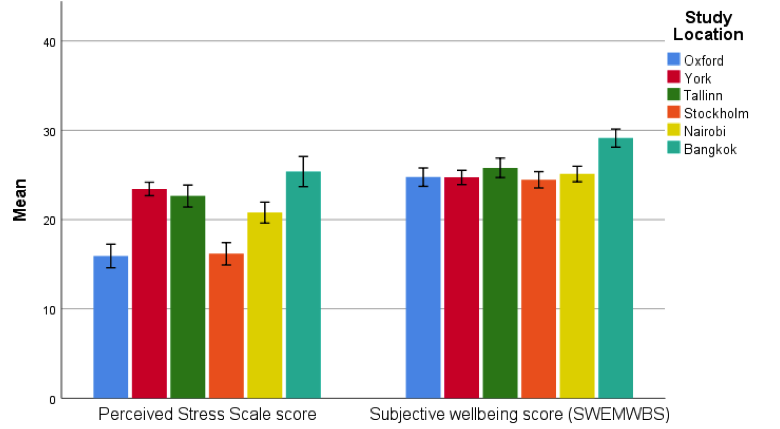
We attempted to apply a standardised framework of analysis in order to compare health and wellbeing metrics between adults in Europe, Africa and South East Asia in order to understand any health and wellbeing differences between geographically, socially and economically diverse cities.
Our study’s contribution
This study indicates regional differences in subjective stress and wellbeing and the impact that both green and public spaces may have on these metrics. It adds a direct cross-cultural examination previously somewhat lacking in the literature.
Impacts for city policy and practice
This research addresses the impact of different types of urban space on health and wellbeing across various global cities, as well as understanding specific local issues that may mediate these effects. Our approach provides a solid base for future cross-cultural research using mixed methods and a multi-disciplinary approach to understanding environmental impacts on human health.
Further information
Chris Neale, Mònica Coll Besa, Sarah Dickin, Vanessa Hongsathavij, Piret Kuldna, Cassilde Muhoza (@cassildemuhoza), Pin Pravalprukskul, & Steve Cinderby (@s_cinderby_SEI)
Full research article:
Related posts
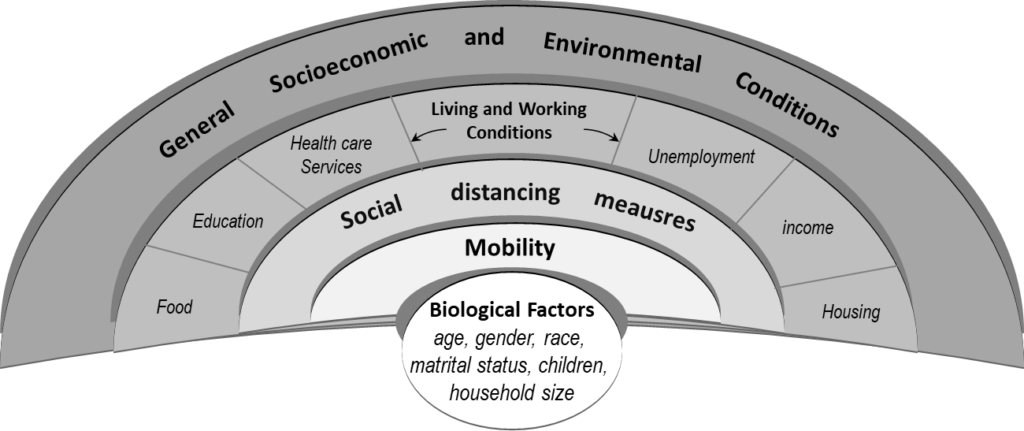
The psychological impact of social distancing order during the COVID-19 pandemic can be determined by combining the effects of both individual and community capacities. This study supports the need to improve the physical environment to implement more sustainable health policies in different communities and cities across the world.

A study of apartment residents identified an association between construction defects and mental health. For every additional problem, wellbeing decreased and psychological distress increased.

I use the travelogue methodology to investigate urban health and sustainable development in relation to the Mekong River in northeastern Thailand, revealing new insights and bringing travel to urban areas near the river into knowledge production.