City Know-hows
Target audience
Landscape architects, environmental educators, city planners and sustainability practitioners and scientists
The problem
There is no established agenda to create sustainable urban environments that combine bio-physical and socio-cultural dimensions. Consequently, many urban environments suffer from lack of direct nature experiences, insufficiently integrated ecosystem services, and narrowly considered public health and well-being in the urban design.
What we did and why
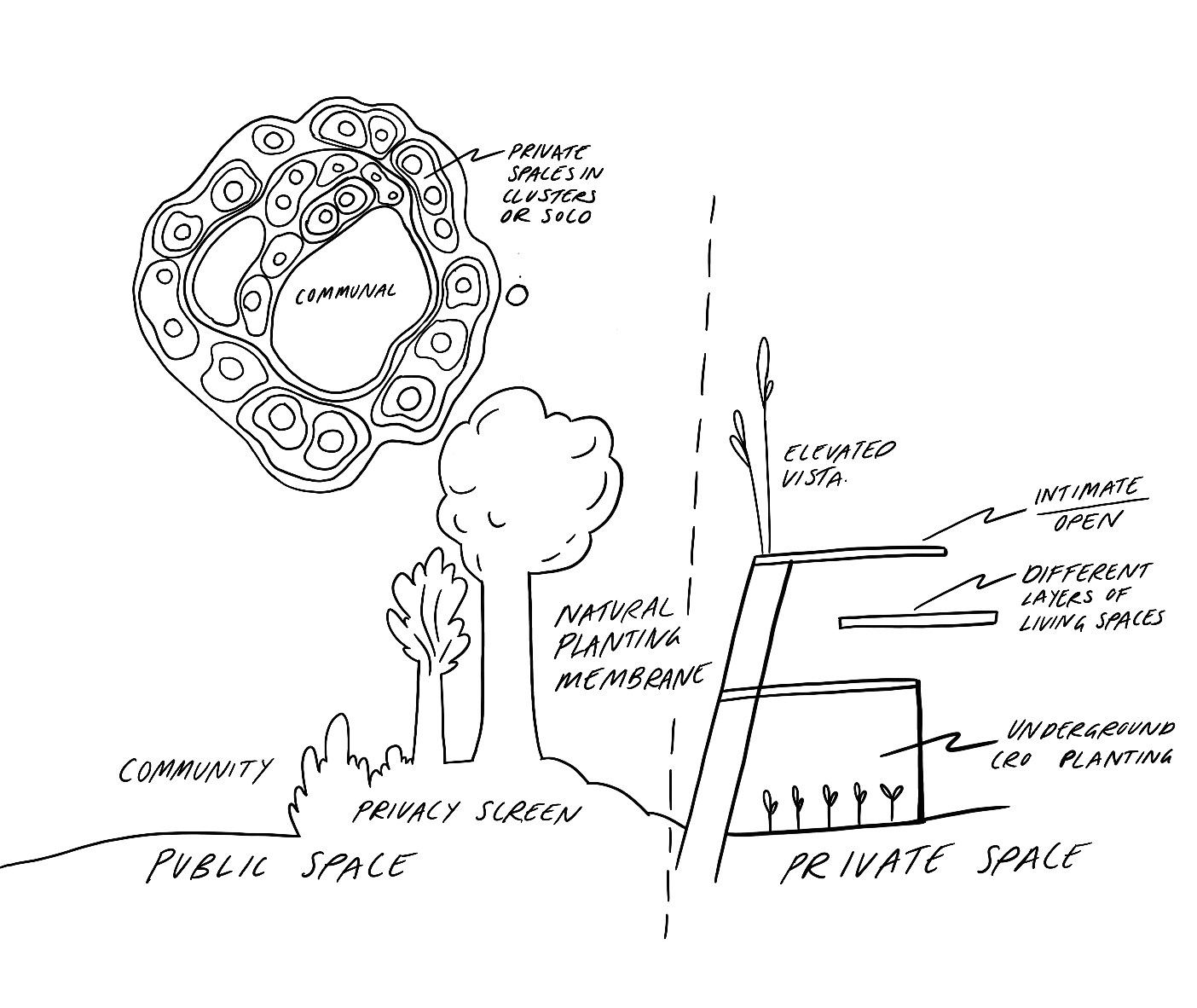
We explored the basis of a transdisciplinary agenda for nature-connecting human habitat, i.e. an ecologically sustainable habitat that promotes a cultural connection between people and nature. We create an explorative vision for sustainable human habitats that integrate personal, social, and environmental factors and then identify actions and synergies to achieve it.
Our study’s contribution
The collective vision suggests a variety of psychological, physical, cultural, and environmental attributes that interplay with each other. Next door nature routines are essential to create nature-connecting habitats. The consequent co-benefits with nature-based solutions are many as is the potential to support the Sustainable Development Goals.
Impacts for city policy and practice
Given the wide range of actors benefitting, further exploration and planning of future human habitats would benefit from including many different actors such as local officials, educators, lawyer, ecologists, landscape architects, and even medical doctors – through social prescribing; and of course, local communities!
Further information
Full research article:
Full research article: Connecting land. A transdisciplinary workshop to envision a nature-connecting human habitat by Matteo Giusti (@matteogiusti), Wenpei Wang & Tanya Marriott. City Know-how editor: Marcus Grant
Related posts

Our study analyzes the impact of COVID-19 on Hong Kong’s progress towards achieving the Sustainable Development Goals. The study identifies four SDGs that stood out with significant impacts from the pandemic. We offer valuable and transferable insights for policymakers and stakeholders involved in pandemic recovery and sustainable development efforts.
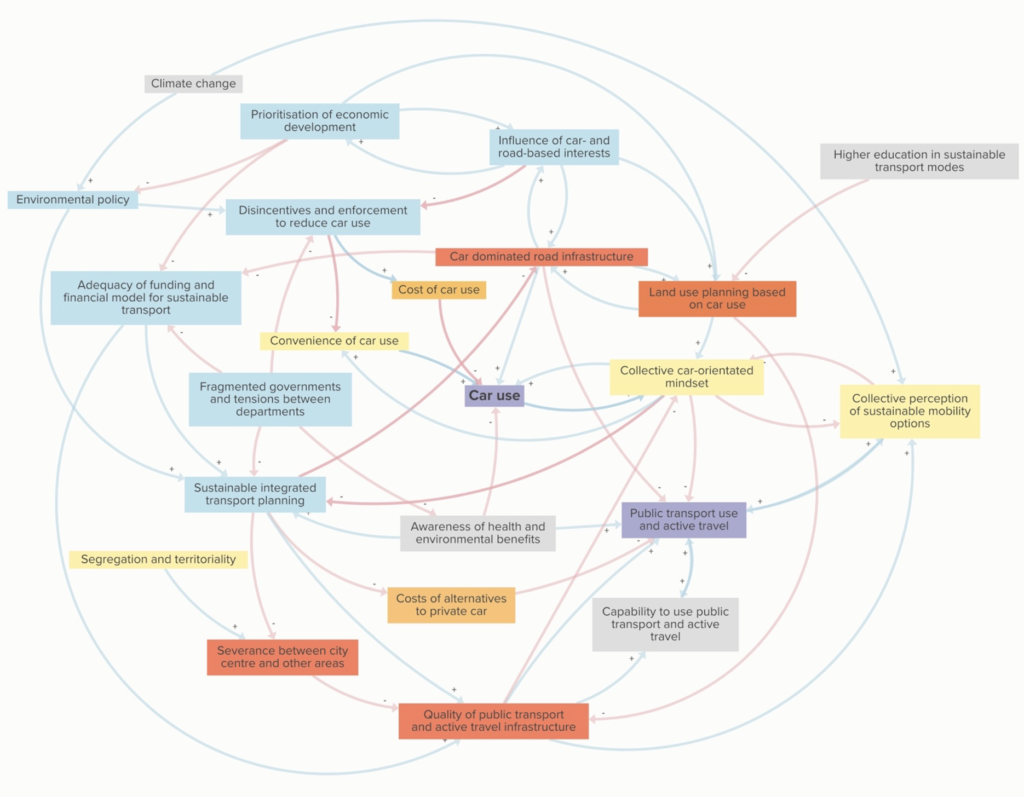
Belfast has very high levels of car use. Working with stakeholders we tried to understand what factors influence this. System wide factors, such as financial models for transport, a collective car-orientated mindset and car dominated road infrastructure, have the strongest influence on individual behaviour.
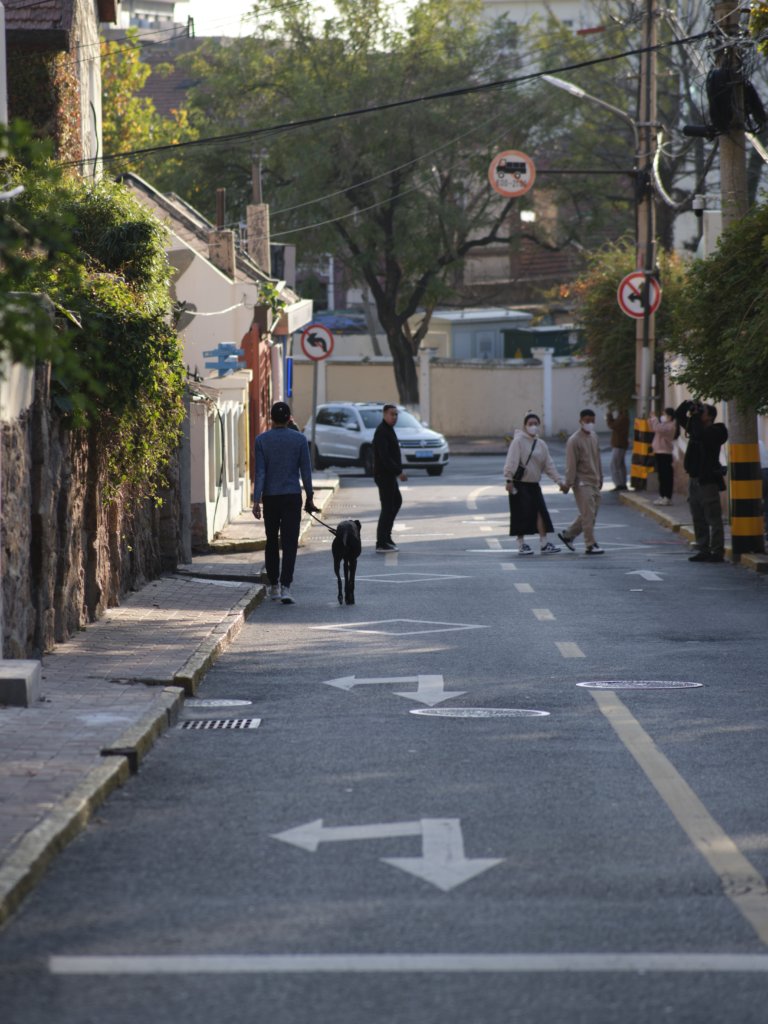

Urban environments influence mental health and development of younger populations. This study explores associations between adolescent mental health indicators and design characteristics. Implications include recommendations for planners and urban designer to promote psychological well-being.