City Know-hows

To create healthy urban places and spaces, public acceptance is key to success.
Share
Target audience
City and municipal planners, public health officials, elected officials at municipal level, health promotion practitioners, citizens
The problem
Poor eating habits and physical inactivity are linked to rising rates of obesity and related chronic conditions. The built environment plays a significant role in shaping these behaviours. To be effective, interventions and policies that transform the built environment to encourage healthy choices must be accepted by the public. However, the lack of context-specific Canadian data on acceptability highlights the need for further research to guide practice and address public health challenges.
What we did and why
We examined the level of agreement among adults in two major cities in Saskatchewan, Canada, to implement built environment interventions and policies promoting healthy eating and physical activity. We explored the individual and neighbourhood-level factors that influenced their agreement. We also looked at the effect of the degree of intrusiveness of the interventions, and policies on agreement. The study’s findings will have practical implications for designing more acceptable interventions to promote healthier behaviours in the population.
Our study’s contribution
We found that:
Recently implemented and proposed built environment changes in the cities may have impacted the study’s findings.
Impacts for city policy and practice
We found that:
Although more research is necessary to understand motivational differences between demographic groups, we can suggest cities need to consider the following;
Further information
Full research article:
Acceptability of built environment interventions to improve healthy eating and physical activity among city dwellers in Saskatchewan, Canada: THEPA findings from a local context by Sahana Ramamoorthy, Lise Gauvin, and Nazeem Muhajarine.
Related posts
As emerging challenges have made urban areas increasingly vulnerable, jeopardizing the health and well-being of their inhabitants, resilience should be seen as a pathway for healthy cities and integrated into urban planning practices. This study shows if and how existing indicator frameworks can identify urban systemic vulnerabilities and priorities for resilience building to provide local authorities with evidence crucial in planning for healthy and resilient cities.
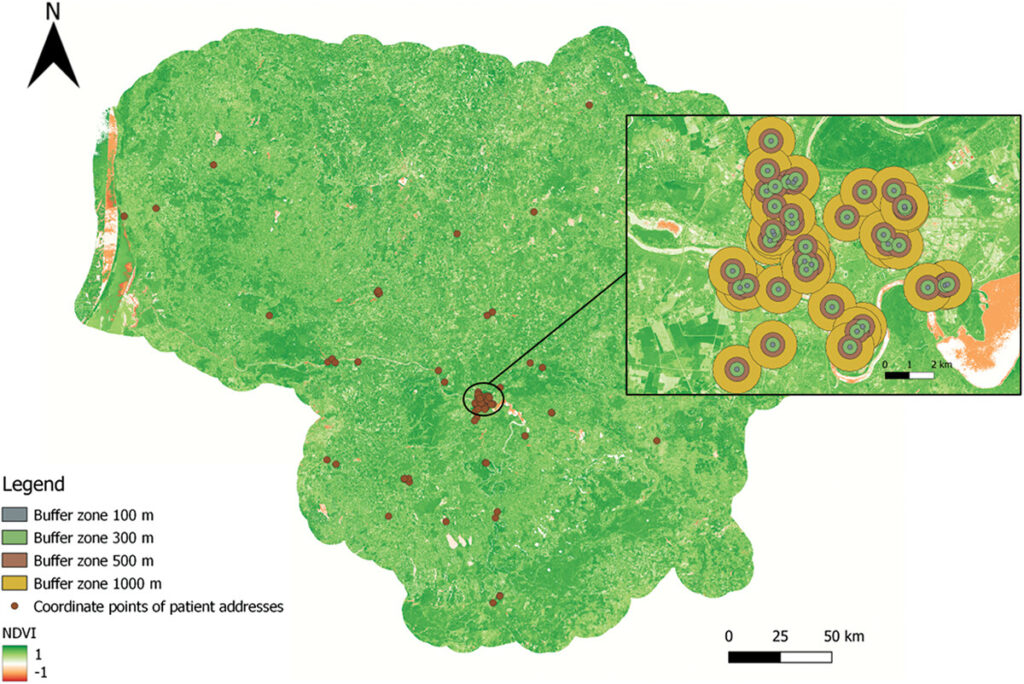
Urban greenness affects people’s physical and mental health. Residential greenness is associated with reductions in cortisol levels after six months in patients with chronic heart failure undergoing rehabilitation.

Livability is a people-oriented concept, and accurately measuring it requires a contextual understanding of what local stakeholders deem essential for making communities livable. Despite extensive research on livability indicators, most studies have taken a top-down approach, with few considering the input of the communities.