City Know-hows

Target audience
Policy-makers, academics, urban planners, environmentalists, traditional title holders, local and international development partners, NGOs and residents.
The problem
Kano is a city with a historic importance attached to the Hausa native trees. Interestingly, some neighbourhoods in Kano actually received their names from native trees. Regrettably, urbanization has seen many of these native trees severely depleted with others disappearing completely from the neighbourhoods that are named after them. It is reported that young people from such neighbourhoods cannot even identify or name such trees at sight, because they don’t know them.
What we did and why
The project restored 17 different native tree species by planting a total of 61 native trees in all the locations where a depleted native tree was though to have stood (neighbourhoods, open spaces, public schools etc.) in order to recreate the historic biophilia of urban Kano. Geographical coordinates of each of the restored trees were taken using hand-held GPS device as a way of tracking the precise location of each restored tree.
Our study’s contribution
This was the first attempt at using innovative lab in Africa to incubate ideas by assembling academics, experts, students and communities to co-design solutions on how to successfully restore some of the depleted native trees in Kano. The findings also highlight the importance of sex-based inclusion in the project, and nature-based solutions in urban ecosystem restoration and sustainability.
Impacts for city policy and practice
Our study findings suggests that the success of project, especially its implementation, cannot be fully and effectively achieved without the inclusion of all stakeholders in the design and policy-decision process.
Further information
See MR CITY LAB. For Millennials to restore urban biodiversity in Kano city through planting of local tree species. Tweeting at @MR CITY LAB
Full research article:
Aliyu Salisu Barau, Kamil Muhammad Kafi, Abubakar Bawa Sodangi & Suleiman Gambo Usman (2020) Recreating African biophilic urbanism: the roles of millennials, native trees, and innovation labs in Nigeria, Cities & Health.
Related posts
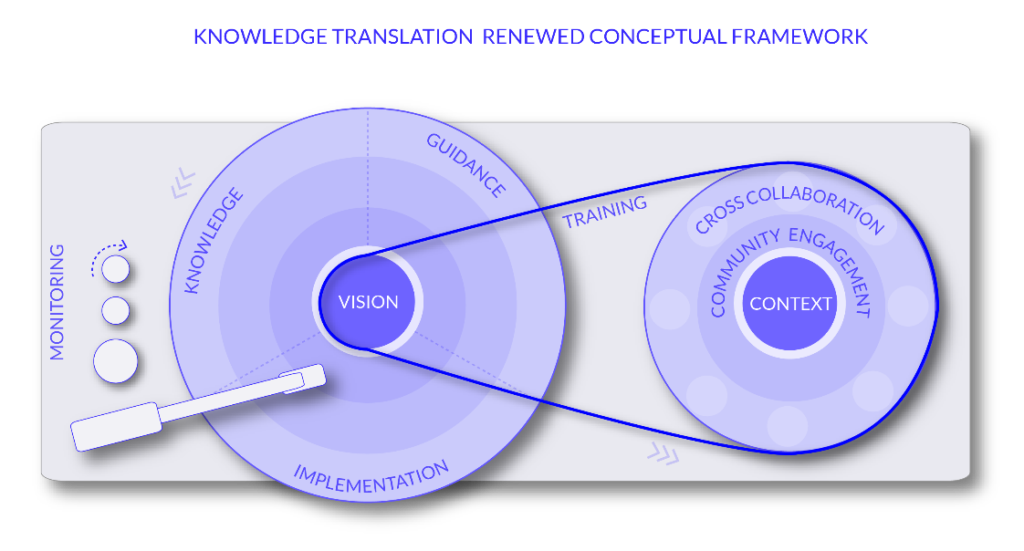
We took a significant step in identifying the existing gaps in knowledge translation for healthy cities and adopting a proactive approach to laying out opportunities for improvement. By developing a visual representation for a renewed conceptual framework, we provide a clear and insightful tool for planners, designers, and policymakers aiming to enhance knowledge translation processes. As a result, this study not only elevates knowledge translation as a field of study for urban professionals but also reinforces its importance in public health.
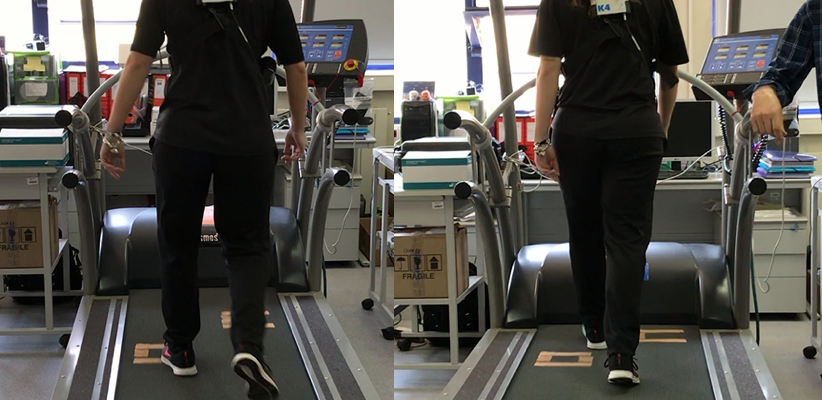

This study measured the effectiveness of stepping stones as an element of landscape design – to make walking a more effective form of exercise for health. The average increase in heart rate due to steppingstones was 17.22%. In conclusion, we estimate that stepping stones can significantly increase peoples metabolic and physiological parameters, and can help the wider population to achieve the recommended government and health guidelines of ‘moderate exercise’ of 150 min/week, improving population health. This new evidence can help designers to implement ‘Active Urbanism’ strategies.

Transportation planners and transit authorities must gain a better understanding of the passenger and ridership experience for those specific demographics who frequently use their services. This understanding can inform future improvements and help transit authorities work towards Universal Design.