City Know-hows
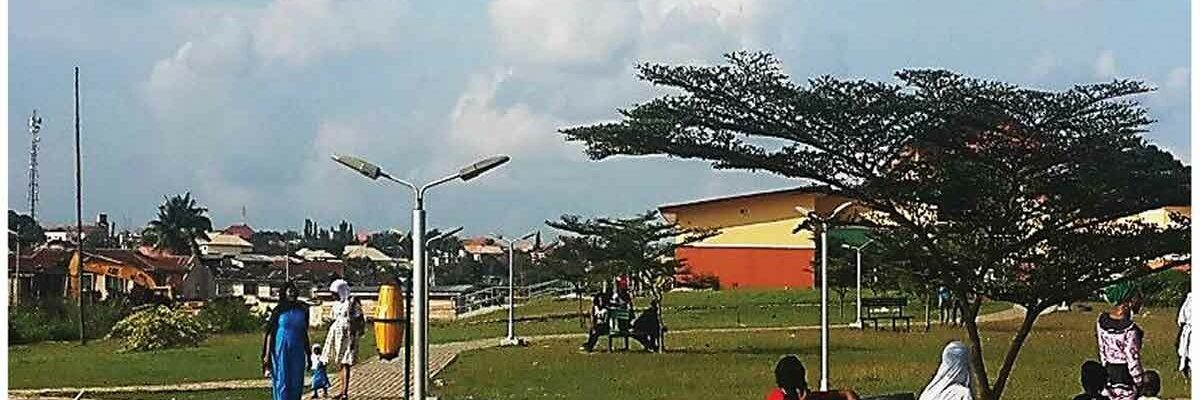

Target audience
Landscape architects, urban designers and planners, public health practitioners and policy makers.
The problem
There is insufficient contextual empirical evidence on the association between open spaces, physical activity, and health in the Global South, particularly in Nigeria. Therefore, it is unknown how open spaces could support behaviours for active living for residents in the region.
What we did and why
We examined the influence of urban open spaces on physical activities in a Southwestern Nigerian City. Our study looked at the relationships among socio-economic characteristics of residents, the attributes and uses of neighbourhood open spaces and self-rated health of residents. We used a cross-sectional survey with 1659 participants in Osogbo, Osun State, Nigeria. Our primary data was collected through questionnaires and direct observations on attributes of open spaces. Secondary data such as maps were also included in data analysis.
Our study’s contribution
We found that most people in the city rarely use open spaces for vigorous or moderate physical activities, instead they prefer to do sedentary activities. However, our results support a socio-ecological theoretical framework that adds insight. In particular, our results showed that:
Age, household size, income and education level significantly influenced residents’ assessment of open space quality,
Physical, stress reduction and social cohesion activities influences the relationship between open spaces and health indirectly,
Open spaces influence residents’ health indirectly through activities performed.
Impacts for city policy and practice
Following our study, we suggests policy and practice should consider:
Urban design interventions that include varied facilities to attract all user groups,
Community based events that encourage residents to get more active should be organised by government and non-government bodies,
Unexploited natural sites in the city should be developed to provide more avenues for healthy lifestyles,
Features that can improve the quality of open spaces and attract all user groups should be provided.
Further information
Not available.
Full research article:
Open spaces and wellbeing: the impact of outdoor environments in promoting health by A. O. Ajayi and O. O. Amole.
Related posts

Our urban environments are getting hotter, yet urban design and planning solutions which can mitigate heat are rarely used. There is a need for further education and strategic planning policy positions to support heat mitigation policy and practice in the built environment.
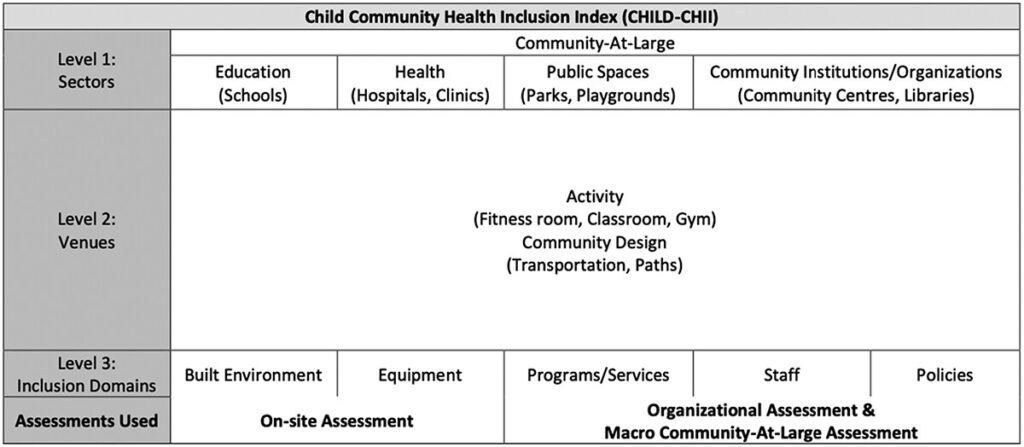
We must take a careful look into the structures, policies, and programs that may be barriers to inclusion of children with disabilities in the community. Assess to intervene and create cities that are inclusive of and healthy for all!

Integrating green spaces into urban planning is crucial for public health. This framework guides cities in evaluating and optimizing their green space strategies to promote health and sustainability, aligning with WHO’s Healthy Cities initiative.