City Know-hows
Target audience
City planners, transportation experts, residents, educators, environmentalists, real estate owners and developers and politicians.
The problem
In a city associated with tension, violence and religion, for those living in proximity to Jerusalem Railway Park, a ‘Rails to Trails’ initiative, can feel like a safe and peaceful bubble. One where users can walk, run, cycle, feel removed from motor traffic, and even imagine that they live in a rural environment. User communities include Arabs and Jews, religious and secular, upper, middle and lower class families, elderly, middle-aged and young.
Yet in this area, physical activity levels meeting the WHO guidelines are especially in low in low to middle socio-economic status communities for adults aged 60 and above
What we did and why
In this study, we sought to understand the perceptions of those 55 and above-aged regarding an environmental change in their neighbourhood. How it frames their lifestyle choices.
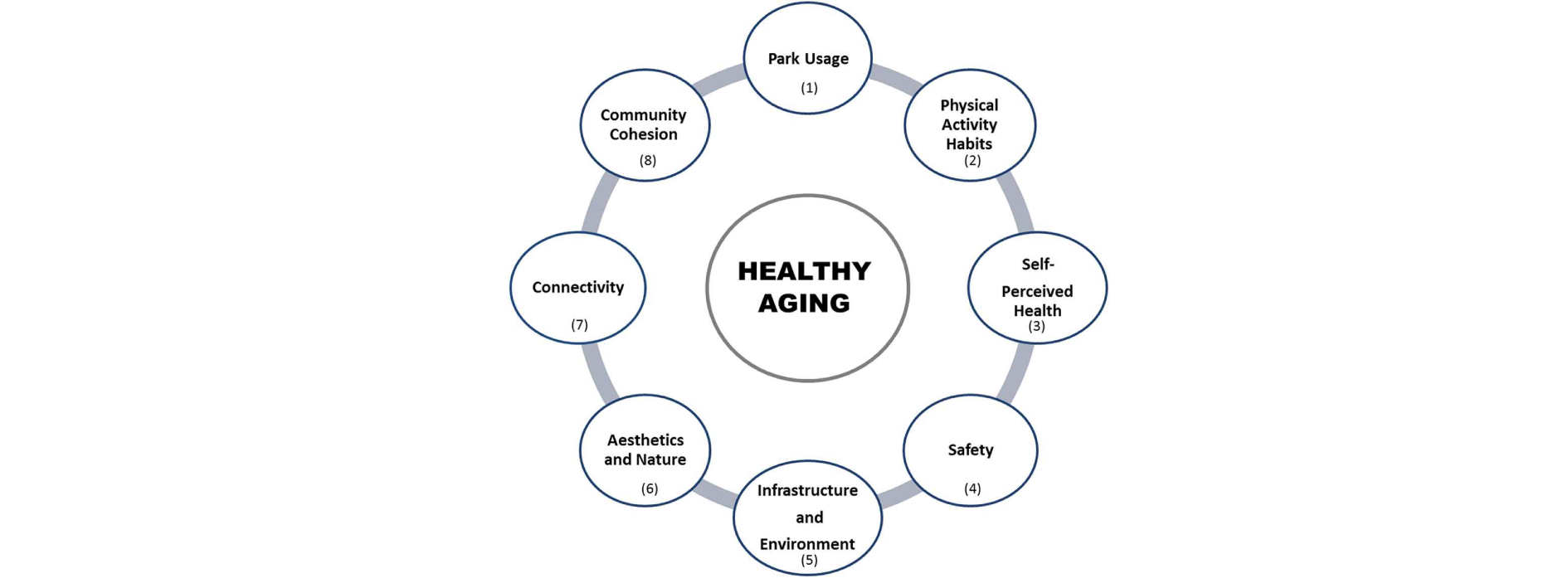
We used a mixed-methods approach to understand how residents of seven diverse nearby neighbourhoods were affected by a renewal this long-abandoned. For this work we created an eight-branched conceptual model capturing the main perceptions raised.
Our study’s contribution
Our study of Jerusalem Railway Park contributes to the understanding of bottom-up community engagement in creating new dialogue between public and municipal authorities for changing urban environment for community health. We also found that:
Impacts for city policy and practice
In terms of practice, our study showed how citizen ownership and creation of feelings of familiarity among the elderly, and respecting history of the place for all local cultures might, can be used as basis for future physical activity interventions; especially among non-active populations or lower-middle income communities. This is also a case study about bridging diverse communities using the common goal of working towards healthy and safe cities for all.
Further information
Full research article:
‘Greening our backyard’- health behavior impacts of the built environment within the overall ecology of active living by Greenshtein, Osnat Keidar, Chariklia Tziraki & David Chinitz. Editor: Marcus Grant.
Related posts
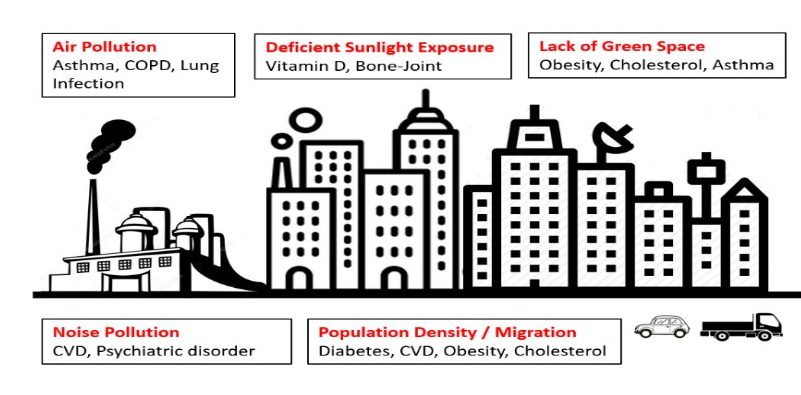
New research on India’s ageing population reveals urban-rural disparities’ impact on health. Urban areas see high rates of obesity, cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and high cholesterol. Urgent call for urban planning and health policies

Understanding how urban environments affect health is the first step in making a healthy city.
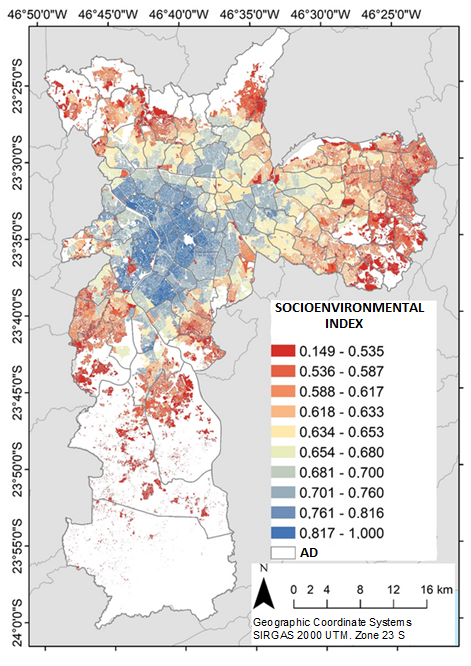
Monitoring slum health through ecological deprivation indexes is a useful strategy to understand and reduce health inequalities within a city. We developed a robust socioenvironmental index capable of explaining health outcomes in small intraurban areas and differentiating areas with the presence of different slum typologies and non-slum spaces.