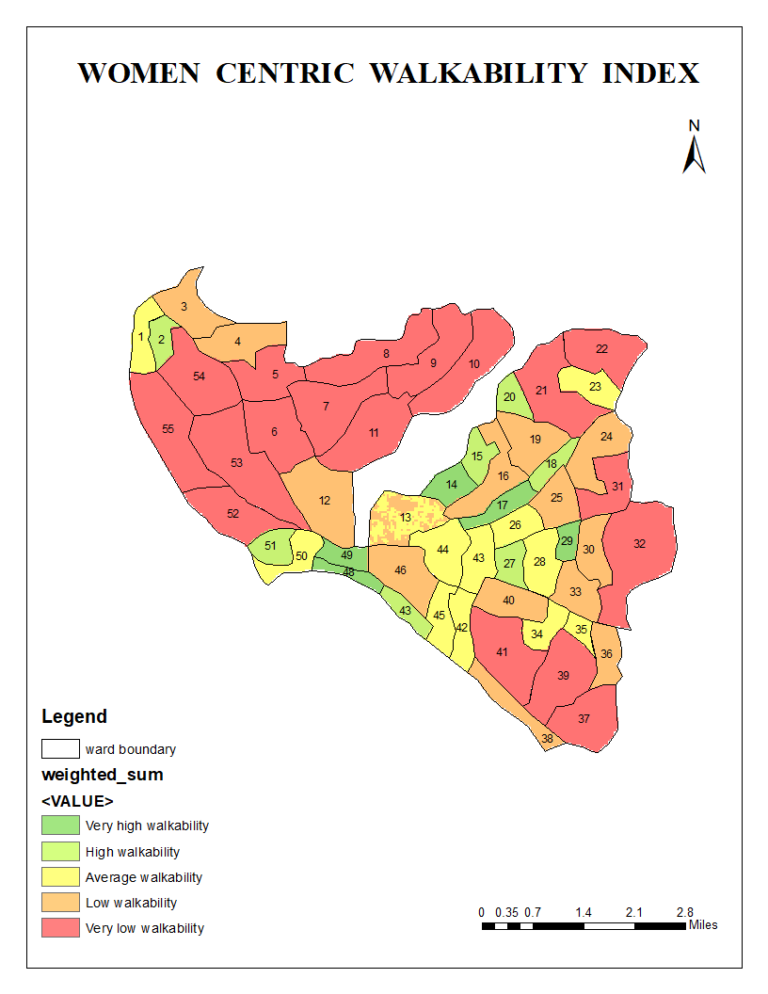
Making streets safer for women: A women-centric walkability index for Kollam’s urban future, India
This study introduces the Women-Centric Walkability Index, addressing factors influencing women’s walking experiences in urban areas. Analyzing fifty-five wards in Kollam Corporation, Kerala, we identified key indicators like well-maintained sidewalks, street lighting, safety measures, and access to public amenities that enhance women’s walkability. Using the Analytical Hierarchy Process and GIS analysis, our research highlights the need for safer, more accessible, and comfortable walking environments for women, benefiting all pedestrians.