City Know-hows
Target audience
World Health Organization; National public health officials; Local and community public health experts.
The problem
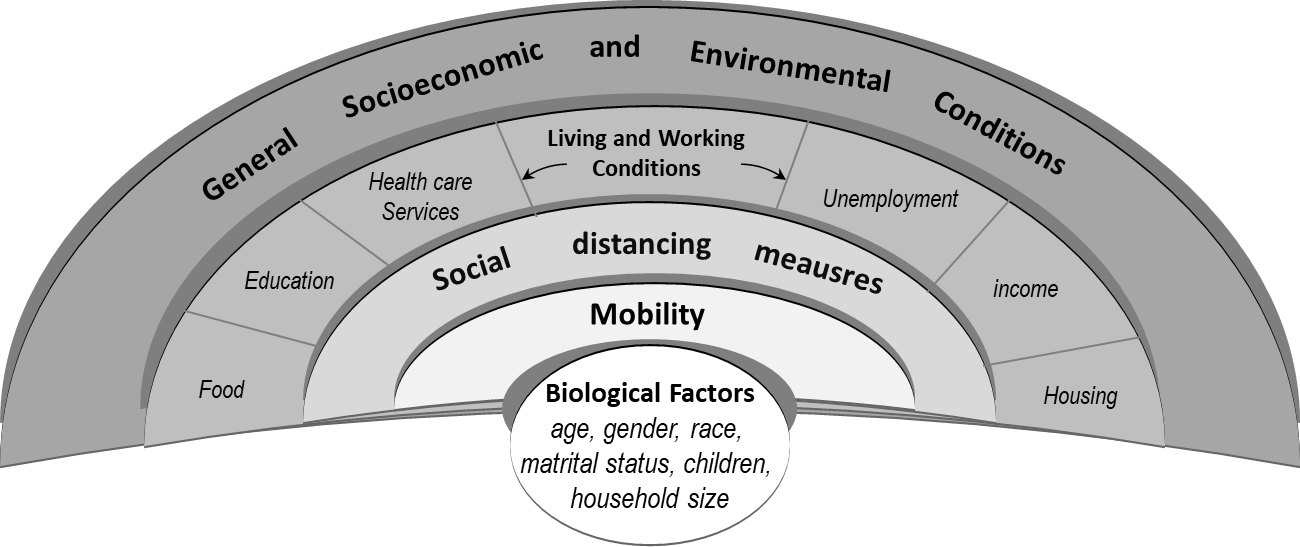
Early COVID-19 studies found relationships between social distancing and mental health problems (anxiety and depression) but their complexity in the contexts of unequal individual capacity and uneven community attributes remains untested.
What we did and why
To reveal the complexity in terms of health inequity, we used a series of statistical models, plus nationally representative and COVID-19-specialized data from the Household Pulse Survey administered by the U.S. Census Bureau between April 23, 2020, and June 7, 2021.
Our study’s contribution
We found that:
Lack of community capacities during the pandemic (e.g. poverty and transit use) and individuals’ economic vulnerabilities (e.g. income loss, food insufficiency, housing instability) exacerbated mental illnesses as social distancing measures were prolonged
A more stringent stay-at-home order was found to be related to an increased risk of experiencing anxiety, depression, and their comorbidity.
The negative impact of the stay-at-home order on mental illnesses is unequal across subpopulation groups of different ages, races and ethnicity, income, and household size
Impacts for city policy and practice
Our findings suggest that:
the psychological impact of social distancing order can be determined by combining the effects of both individual and community capacities.
Our study, which supports others, demonstrate the need to improve the physical environment to implement more sustainable health policies in different communities and cities across the world
Further information
U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): Official indicators of anxiety and depression during the COVID-19 pandemic in the U.S.
Full research article:
Understanding the community and social determinants in mental health inequity: the impact of mass social distancing during the COVID-19 pandemic by Jin Hui Lee, JungHo Park & Min Sook Park
Related posts

Understanding of the influence of local political actors helps to highlight where their influence is limited, particularly by national-level housing policy, which in the UK is focused on housing numbers, rather than quality of new homes, as well as financial viability and public opinion. Understanding this can help to build trust in the political processes of decision-making and inform interventions for healthier place-making.
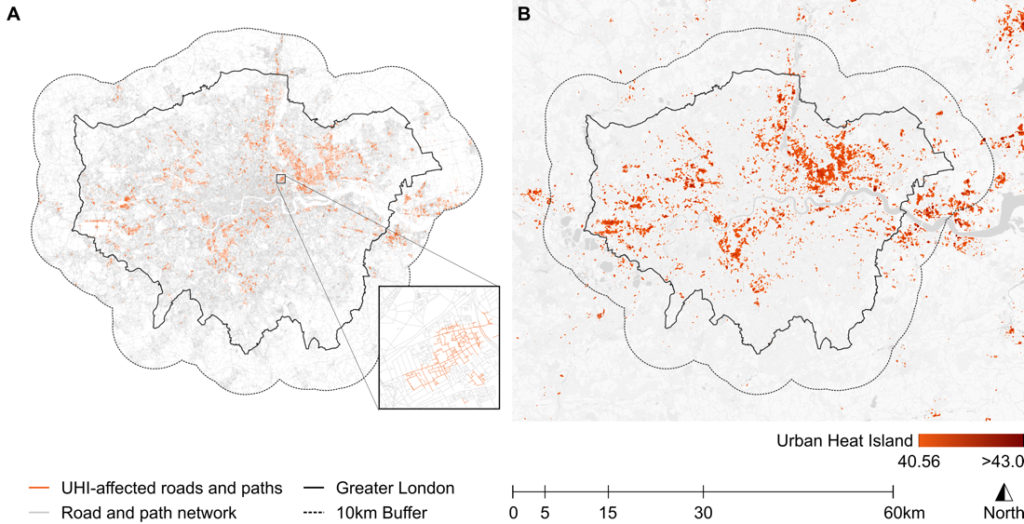
Our research highlights how some groups in London, like children, ethnic minorities, and lower-income residents, experience hotter areas due to the Urban Heat Island effect. We provide a clear approach for local governments to make climate action fairer and more effective.

Urban environments in many cities, both those found in Mexico and many other countries, can be called obesogenic – they are prone to promote obesity. Relevant factors are that they foster sedentary behaviour, poor dietary choices, and elevated stress levels; thus contributing to higher obesity rates. Urban planning, design, and practices offer opportunities for upstream public health interventions to mitigate these negative health impacts. These findings are especially relevant given the role of neighbourhood environments in encouraging children’s physical activity and reducing obesity.